-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 7
Externals
This topic contains the following examples:
- Outsourcing a document library
- Access an external class
- Create a derived class from an external class
- Import an external class
These code examples show how to work with external referenced documents using the Aml.Engine and the service extension Aml.Engine.Services. Minimum engine version to use these examples is version 3.1.5.
The SplitService is used in the examples to outsource libraries into external documents. The ExternalReferenceResolver service is used to resolve references which address CAEX-objects in outsourced external documents. The ExternalReferenceResolver can load documents if the path, defined in the ExternalReference element is accessible. Local files as well as web resources can be loaded.
In this example the standard AutomationML RoleClassLibrary is outsourced into an external document using the SplitService. A RoleClass, contained in the outsourced library, is assigned to a SystemUnitClass.
using Aml.Engine.AmlObjects;
using Aml.Engine.CAEX;
using Aml.Engine.CAEX.Extensions;
using Aml.Engine.Services;
using Aml.Engine.Services.Interfaces;
public CAEXDocument OutsourceLibrary()
{
// creates an empty CAEX document
var document = CAEXDocument.New_CAEXDocument();
// registration of the split service
var splitService = SplitService.Register();
// Add the AutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib to the document and mark the library as a split point
splitService.SetSplitPoint(document.AddAutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib());
// Append a SystemUnitClass referencing the standard Resource-RoleClass
var s1 = document.SystemUnitClassLib.Append("slib").SystemUnitClass.Append("s1");
s1.AddRoleClassReference(AutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib.Resource);
// Outsource the AutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib to an external file
splitService.Split(document, alias:"Base", filePath:"./base.aml");
// Remove the SplitService from the Service Registration
SplitService.UnRegister();
// When the split is executed, the document contains a new external reference with
// the provided 'alias' and 'path'. The RoleClassLibrary is removed from the document.
// The reference to the roleClass is changed to a reference with the defined alias.
// This is checked with the following assertions.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Assert.NotNull(document.ExternalReferenceFromAlias("Base"));
// Assert.IsNull (document.RoleClassLib[0]);
// Assert.AreEqual ("Base@AutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib/AutomationMLBaseRole/Resource",
// s1.SupportedRoleClass[0].RefRoleClassPath);
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
return document;
}In this example an external class contained in the previously outsourced library is accessed. To access the class, the ExternalReferenceResolver service is needed.
using Aml.Engine.AmlObjects;
using Aml.Engine.CAEX;
using Aml.Engine.CAEX.Extensions;
using Aml.Engine.Services;
using Aml.Engine.Services.Interfaces;
public void AccessExternalRoleClass()
{
// use the CAEX document from the previous example
var document = OutsourceLibrary();
// To work with external classes, the ExternalReferenceResolver is needed
var externalsResolver = ExternalReferenceResolver.Register();
// Get the systemUnitClass
var s1 = document.SystemUnitClassLib["slib"]["s1"];
// Get the supported roleClass, this roleClass is found by the ExternalReferenceResolver in the
// outsourced library.
var roleClass = s1.Roles.First();
// The following assertions hold
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Assert.IsNotNull(roleClass);
// Assert.AreNotEqual(roleClass.Document, s1.Document);
// Assert.IsTrue (externalsResolver.IsExternal(roleClass.Node, out var alias));
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// add a child systemUnitClass
var s1_1=(SystemUnitFamilyType) s1.AddChild("s1_1");
// assign the external roleClass to the systemUnitClass
s1_1.AddRoleClassReference(roleClass);
// The roleClass is recognized as an external Object and the reference to the class
// is created including the alias of the external document
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Assert.AreEqual("Base@AutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib/AutomationMLBaseRole/Resource",
// s1_1.SupportedRoleClass[0].RefRoleClassPath);
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Add a new RoleClass Library with a new role derived from the external role
var myResource = document.RoleClassLib.Append("rLib").RoleClass.AppendWithReference(
"myResource", referencedClass:roleClass, out var isReferenced);
// The assertions check, wether the reference is created and defined with an alias
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Assert.AreEqual("Base@AutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib/AutomationMLBaseRole/Resource",
// myResource.RefBaseClassPath);
// Assert.IsTrue(isReferenced);
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
}In this example a new RoleClass is created with a relation to an external base class contained in the previously outsourced library. To access the class, the ExternalReferenceResolver service is needed.
using Aml.Engine.AmlObjects;
using Aml.Engine.CAEX;
using Aml.Engine.CAEX.Extensions;
using Aml.Engine.Services;
using Aml.Engine.Services.Interfaces;
public void DeriveFromExternalRoleClass()
{
// use the CAEX document from the first example
var document = OutsourceLibrary();
// To work with external classes, the ExternalReferenceResolver is needed
var externalsResolver = ExternalReferenceResolver.Register();
// Find the 'Resource'-RoleClass in the external document.
// Variant 1: Use the alias path and search from the document.
// The alias path is formatted using string interpolation and defined constants
var path = $"Base{CAEXPathBuilder.AliasSeparator}{AutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib.Resource}";
var roleClass = document.FindByPath (path) as RoleFamilyType;
// Variant 2: Locate the external document and use the standard path
var (Document, Message) = externalsResolver.LoadOrGetReferencedDocument(document.ExternalReferenceFromAlias("Base"));
if (Document == null)
{
Console.WriteLine(Message);
}
else
{
// the document_a ist the document, containing the external library
roleClass = Document.FindByPath(AutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib.Resource) as RoleFamilyType;
}
// To get the external reference by an alias an indexed access is also possible
// var extRef = document.CAEXFile.ExternalReference[(CAEX_CLASSModel_TagNames.ALIAS_ATTRIBUTE, "Base")];
// Add a new RoleClassLibrary with a new RoleClass, derived from the external RoleClass
// The RoleClass "myRessource" gets a reference to the external Resource-RoleClass
var myResource = document.RoleClassLib.Append("rLib").RoleClass.AppendWithReference(
name:"myResource", referencedClass:roleClass, out var isReferenced);
// The assertions check, wether the reference is created and defined with an alias
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Assert.AreEqual("Base@AutomationMLBaseRoleClassLib/AutomationMLBaseRole/Resource",
// myResource.RefBaseClassPath);
// Assert.IsTrue(isReferenced);
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
}In this example an external class contained in an outsourced library is imported into the document. To access the class, the ExternalReferenceResolver service is needed. The following configuration is created for the implementation example.
The external documents Document_A with classes CA1 and CA2 and Document_B with class CB1 are used. The class CA1 in Document_A is a derivation of the class CB1 from Document_B (the reference is noted as RefB@CB1 with RefB defining the alias name of Document_B). In Document_A, CA2 is a derivation of the class CA1.
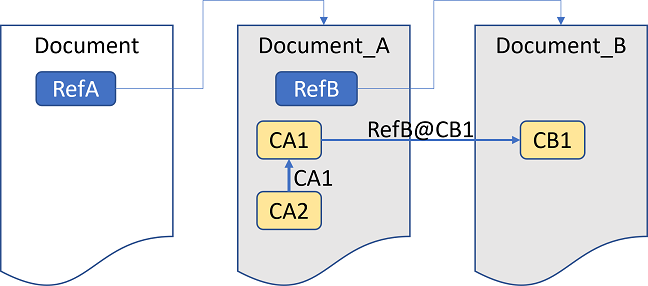
In the first example, the class named CA2 is to be imported from Document_A. During the import, a copy of the class is created and the reference to the base class CA1 is converted to the external reference RefA@CA1, since the base class is not imported as well.
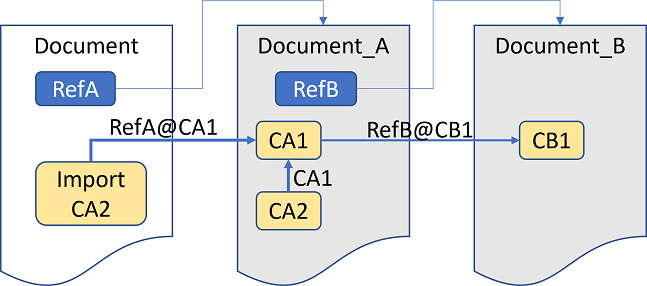
In the second example, the class CA1 is to be imported from Document_A. Since CA1 has the reference RefB@CB1 to class CB1 from Document_B, a new external reference to Document_B with the same alias name RefB is added in the importing document, since the external base class is not imported as well. Please note that the alias name is kept so that the copied references remain valid unchanged. A problem may occur if the alias name in the target document is already used for an external reference to another document. In this case, a new unique alias name is generated and the references are updated.

using Aml.Engine.AmlObjects;
using Aml.Engine.CAEX;
using Aml.Engine.CAEX.Extensions;
using Aml.Engine.Services;
using Aml.Engine.Services.Interfaces;
public void ImportExternalsTest()
{
// create the external documents as defined for this example
using (var document = CAEXDocument.New_CAEXDocument())
{
var aLib = document.SystemUnitClassLib.Append("ALib");
bLib = document.SystemUnitClassLib.Append("BLib");
var cb1 = bLib.SystemUnitClass.Append("CB1");
var ca1 = aLib.SystemUnitClass.AppendWithReference("CA1", cb1, out var isReferenced);
var ca2 = aLib.SystemUnitClass.AppendWithReference("CA2", ca1, out isReferenced);
var splitService = SplitService.Register();
splitService.SetSplitPoint(bLib);
splitService.Split(document, alias: "RefB", filePath: "./document_b.aml");
document.SaveToFile ("./document_a.aml", true);
SplitService.UnRegister();
}
using (var document = CAEXDocument.New_CAEXDocument() )
{
// prepare the document to access classes from document_a
var refa = document.CAEXFile.ExternalReference.Append();
refa.Path = "./document_a.aml";
refa.Alias = "RefA";
// To work with external classes, the ExternalReferenceResolver is needed
var externalsResolver = ExternalReferenceResolver.Register();
// Get the external document
var (Document, Message) = externalsResolver.LoadOrGetReferencedDocument(refa);
// locate the classes to be imported
var ca2 = Document.FindByPath("ALib/CA2");
var ca1 = Document.FindByPath("ALib/CA1");
// simply call the standard insert method to import the external class ca2
// the reference to the BaseClass is updated
document.SystemUnitClassLib.Append("Lib").Insert (ca2);
// These assertions are true
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Assert.AreEqual(document.SystemUnitClassLib["Lib"]["CA2"].RefBaseClassPath, "RefA@ALib/CA1");
// Assert.AreEqual(document.SystemUnitClassLib["Lib"]["CA2"].BaseClass, ca1);
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// simply call the standard insert method to import the external class ca1
// an additional ExternalReference is created to reference the BaseClass
document.SystemUnitClassLib["Lib"].Insert(ca1);
// These assertions are true
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Assert.IsNotNull(document.ExternalReferenceFromAlias("RefB"));
// Assert.IsNotNull(document.FindByPath(document.SystemUnitClassLib["Lib"]["CA1"].RefBaseClassPath));
// Assert.AreEqual(document.SystemUnitClassLib["Lib"]["CA1"].BaseClass.Name, "CB1");
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
}
}Home | Installation | API | Solutions
Getting Started
- Install
- First Steps with CAEX
- Working with CAEX Libraries
- Working with CAEX Relations
- Managing Inheritance
- Attribut Values
- Document Versions
Extended Examples
API Reference Guide