-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 100
v1.3 0. Home
The CubeSatSim is a low cost satellite emulator that runs on solar panels and batteries, transmits UHF radio telemetry, has a 3D printed frame, and can be extended by additional sensors and modules. This project is sponsored by the not-for-profit Radio Amateur Satellite Corporation, AMSAT®.
This page is for the new beta v1.3 hardware.
If you have the v1.0, v1.1, or v1.2 hardware, use these instructions

Here you will find documentation about this project and detailed install instructions.
The CubeSatSim has the following features:
- Working solar panels and rechargeable batteries
- Multi-channel voltage, current, and temperature telemetry transmitted in the Amateur Radio UHF band
- Telemetry decoding using FoxTelem software or APRS software
- STEM Payload board with Raspberry Pi Pico microcontroller & sensors
- Tape measure monopole, dipole, or SMA antenna
- Integrated Low Pass Filter
- 3D printed frame and solar panels
If you don't have the time or money to build a CubeSatSim that transmits real telemetry, you can build a CubeSat Simulator Lite.
Here are the changes between the v1.2 and the v1.3 hardware and software:
These improvements are available to new v1.3 CubeSatSim builders or A v1.0, v1.1, or v1.2 CubeSatSims which are upgraded with a new STEM Payload board and software upgrade:
- FM transceiver module for better frequency stability and simple command receiver to control beacon
- Replace Pro Micro microcontroller with the more modern and cheaper Raspberry Pi Pico
- Callsign and battery voltage text overlay on SSTV images
These improvements are available to new v1.3 CubeSatSim builders:
- Redesigned for blue INA219 voltage and current sensors instead of more expensive purple ones
- Battery board now has integrated voltage and current sensor and PTC fuse with better performance
- Simpler charging circuit with no boost converter or charge controller
- Can be modified to fly as a balloon payload with 500mW FM output for SSTV, APRS, or CW transmissions
- Support for serial GPS module
- Kits can be built with through hole parts. Fully assembled boards will be available in the future with SMT parts
- Parts easier to source (e.g electronics distributors and Amazon) with easy to find solar panels. New BOM uses Octopart electronic part inventory site with one click distributor ordering
- QwIIC connectors for easily adding sensors to the Raspberry Pi Zero or Raspberry Pico
Here are the four boards that make up the complete board stack. Left to right: Raspberry Pi Zero WH, Main Board, Battery Board, and STEM Payload Board.

Here is the built board stack:

There is a 3D printed frame, including solar panels:

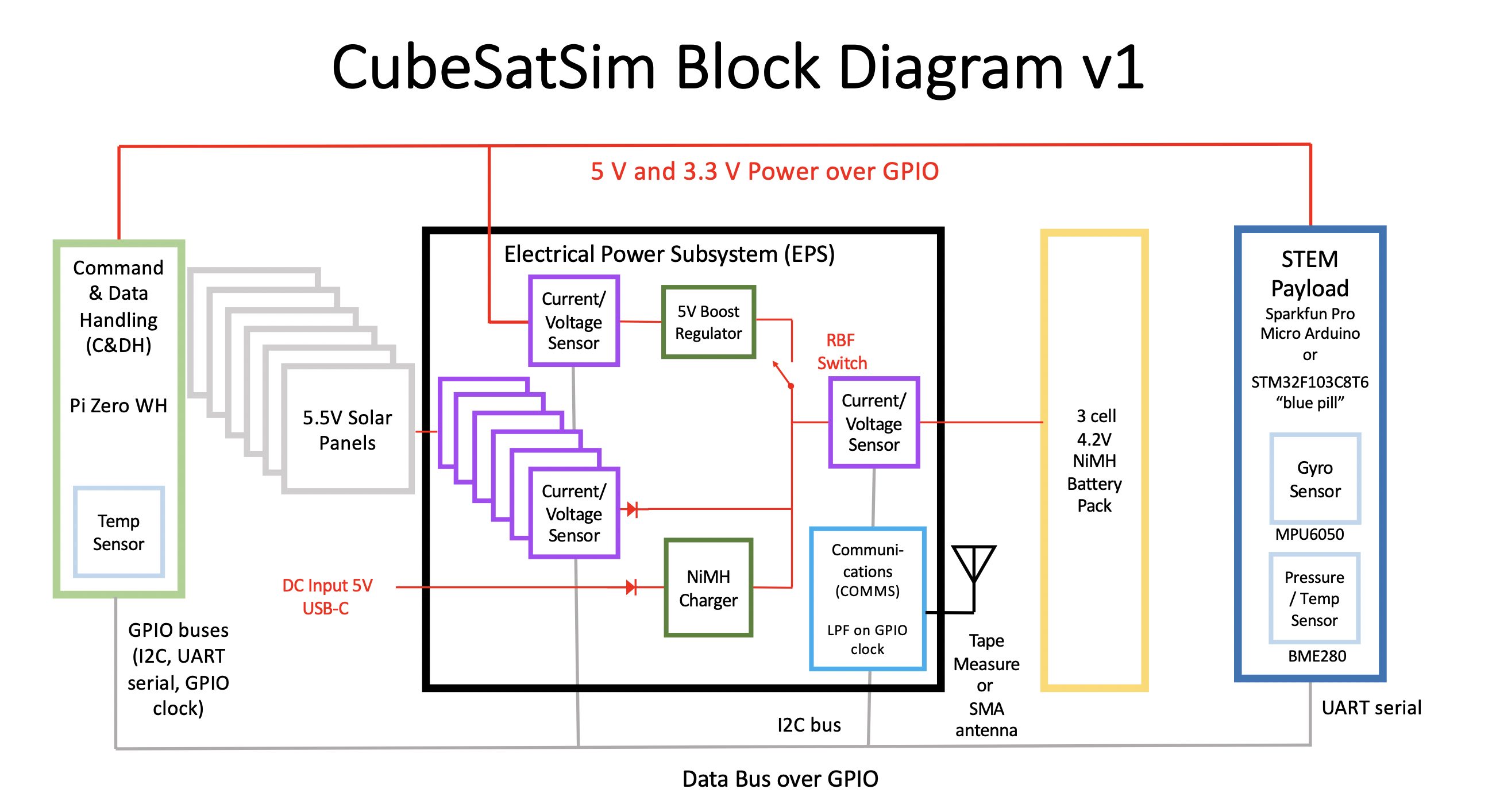
Here is a block diagram of the design:
Parts List to build the CubeSatSim is available here http://cubesatsim.org/bom
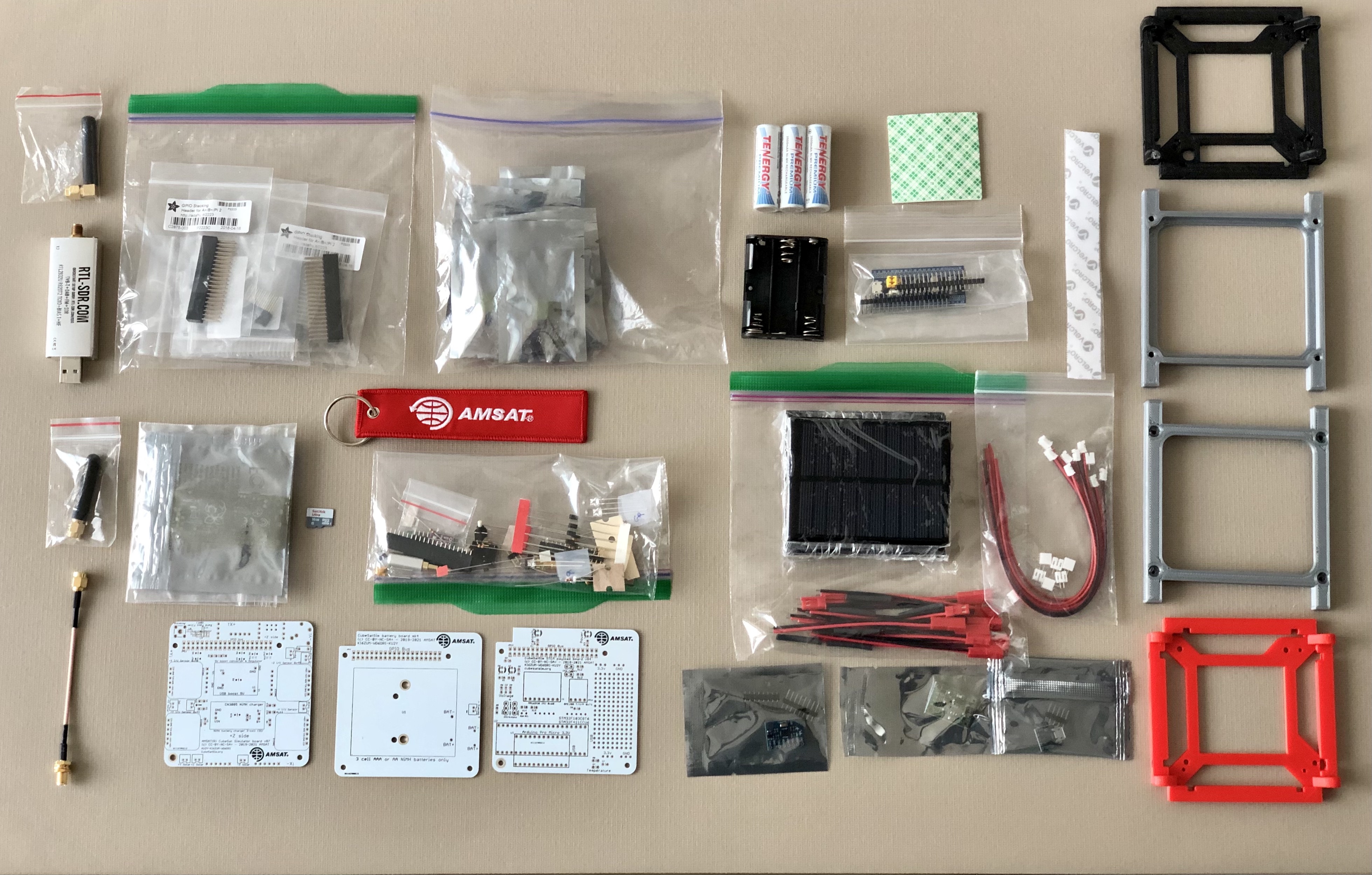
Here is a photo of a kit of parts:
Here are the steps to build a CubeSatSim:
1. Build the Main board Part 1
4. Continue Building the STEM Payload board Part 2
6. Assemble the Solar Panels and Frame
8. Put the Board Stack together and mount in the Frame
The BOM has a sheet "By Steps" which lists the parts needed for each step in order. https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1EuUqyKnXduMlDo9ghCWJu1VY-y2_TWXYRR3S3zGaw9s/edit?usp=sharing If you have a Google account, you can make a copy of this spreadsheet ("File" then "Make a Copy") and check off each part as you install it.
Here is a set of videos showing the various steps: