-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 31
1. Software Architecture
The figure below illustrates the overall architecture of CARP Mobile Sensing (CAMS). The runtime model consisting of three main layers; the core runtime (middle layer), deployment and data manager services (top layer), and the sampling packages (bottom layer), which again builds on top of a set of Flutter plugins that access sensors and services in the underlying OS, external wearable devices, and cloud-based services. This architecture is designed to achieve the non-functional software architecture goals of being highly extensible, cross-platform, and maintainable.
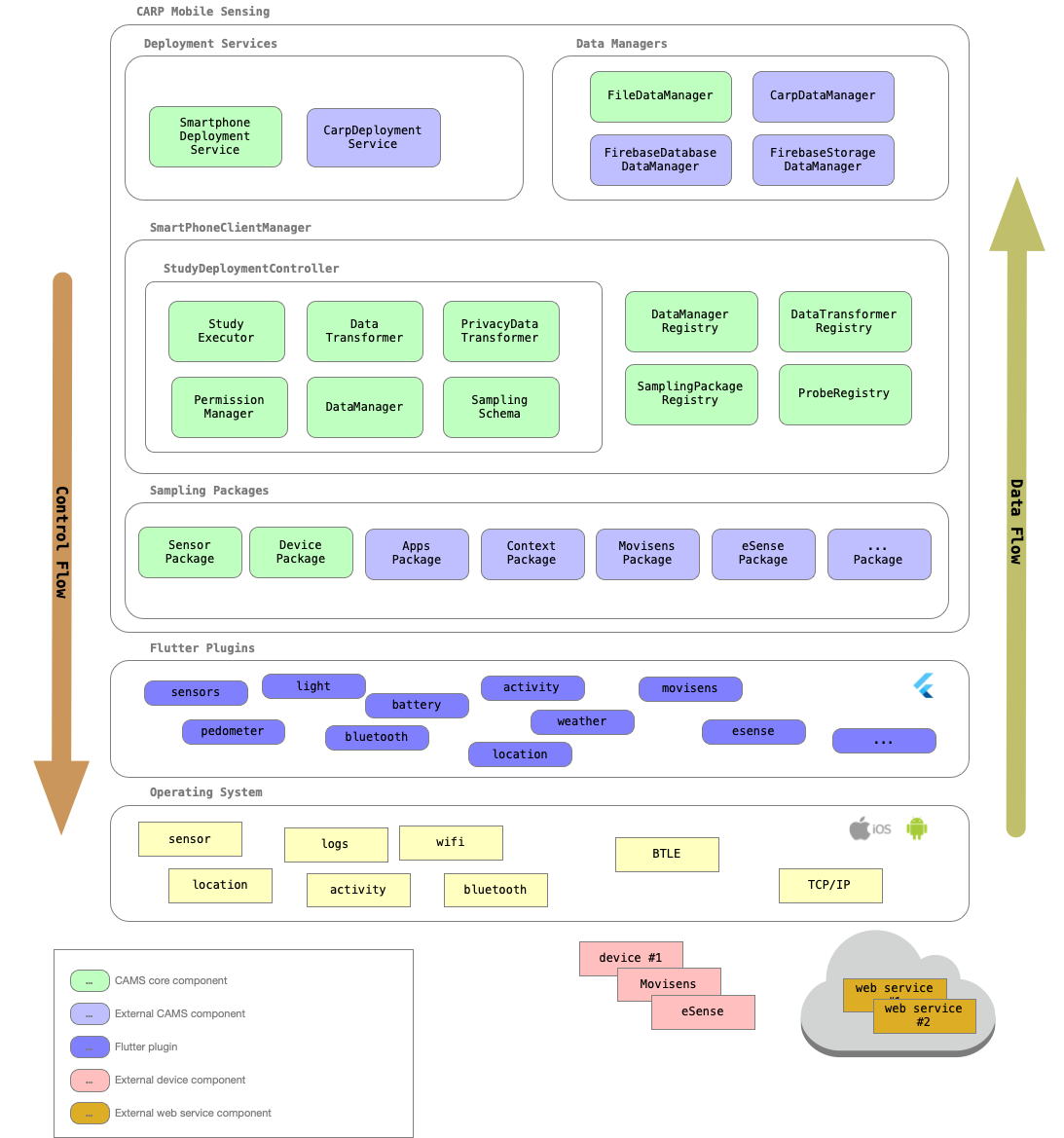
This is the "core" CAMS runtime (the middle layer):
-
The
SmartPhoneClientManagercan run one (or more)StudyDeploymentController, which is based on adding a study to the SmartPhoneClientManager. -
The
StudyDeploymentControllercan be configured by specifying aDataEndPoint(which again loads an appropriateDataManager), along with other settings. Once configured, aStudyDeploymentExecutoris responsible for executing the study deployment. -
The
StudyDeploymentControlleruse a set of registries to look up an appropriate data manager, a set of sampling packages, data transformers, and sensing probes for executing the sensing study deployment protocol.
The service layer (top layer) holds
-
The Deployment Service, which is able to manage and deploy the
StudyProtocol. -
Data manager services, which knows how to store, save, or upload data (e.g., to a file or to Firebase).
The sampling layer (bottom layer) holds
-
A set of
SamplingPackages, which can collect a specific type of measure. CAMS comes with two built-in sampling packages (theDeviceSamplingPackageandSensorSamplingPackage), but most sampling packages are available as external packages which are used in the app, as needed. In this way, an app only needs permissions to access probes (and hence sensors), which are needed in a specific app. Thecarp_context_packageis an example of an externally loaded sampling package, which are available on pub.dev. -
Each sampling package contains one or more
Probes, which can access the underlying sensor and collect the data. Access to sensor data is typically done using a Flutter plugin. Note that these Flutter plugins are external to CAMS and is loaded as needed by the sampling package. For example, thecarp_context_packagemake use of theweatherplugin to access weather data (as a web service).