-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
[DML] SQL Syntax
select * from {table_name};select col1,col2,.. from {tablename};
select distinct col1,col2.. from {table_name};select count(distinct col_name) from {table_name};select Count(*) AS distinctelement from(select distinct col_name from table_name);
select col_name,col_name2 from table_name where {condition};select * from table_name where {condition};- NOTE: single or double quote in text values and no quote in numeric values.
- NOTE: where clause used in select, delete, update etc. statements.
- NOTE: used symobl are <,>,=,>=,<=,<> or ! (not equal),BETWEEN,LIKE,IN.
select * or colname1,colname2.. from table_name where condition AND condition AND condition..;select * or colname1,colname2.. from table_name where condition OR condition OR condition..;select * or colname1,colname2.. from table_name where NOT condition;select * or colname1,colname2.. from table_name where condition AND (condition OR condition);select * or colname1,colname2.. from table_name where NOT condition AND NOT condition;
select * or colname1,colname2,.. from table_name order by colname ASC or DESC;select * or colname1,colname2,.. from table_name order by colname ASC,colname DESC;select * or colname1,colname2,.. from table_name order by colname;select * or colname1,colname2,.. from table_name order by colname,colname2;
insert into table_name(col_name,col_name,..) values("string_value",int_value,..,value);insert into table_name values(value1,value2,value3,...);
select * from table_name where col_name IS NULL;select * or col_name,.. from table_name where col_name IS NOT NULL;
update table_name set col_name=value1,col_name2=value2,.. where col_name=value;update table_name set col_name=value;- NOTE: overwrite all the previous values.
delete from table_name where {condition};delete from table_name;- NOTE: Delete entire data of the table.
- mysql (limit):
select colname,.. or * from table_name where {condition} LIMIT {number}; - mysql (limit):
select * or colname(s) from table_name order by colname ASC | DESC LIMIT {number}; - oracle (fetch):
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name ORDER BY column_name(s) FETCH FIRST number ROWS ONLY;
select min(col_name) from table_name where {condition};select max(col_name) from table_name where {condition};select min(col_name) AS min_column from table_name;
- count:
select count(col_name) from table_name where {condition}; - average:
select avg(col_name) from table_name where {condition};//only for numeric column. - sum:
select sum(col_name) from table_name where {condition};//numeric column.
-
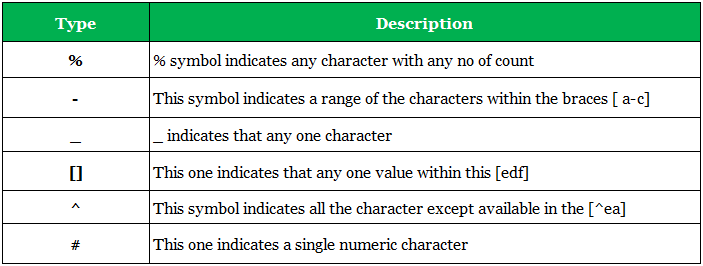
LIKE Operator Description ( All expressions )
-
WHERE CustomerName LIKE 'a%' Finds any values that start with "a"
-
WHERE CustomerName LIKE '%a' Finds any values that end with "a"
-
WHERE CustomerName LIKE '%or%' Finds any values that have "or" in any position
-
WHERE CustomerName LIKE '_r%' Finds any values that have "r" in the second position
-
WHERE CustomerName LIKE 'a_%' Finds any values that start with "a" and are at least 2 characters in length
-
WHERE CustomerName LIKE 'a__%' Finds any values that start with "a" and are at least 3 characters in length
-
WHERE ContactName LIKE 'a%o' Finds any values that start with "a" and ends with "o"
-
select col_name,.. from table_name where col_name LIKE '{expression}'; -
select col_name,.. from table_name where col_name NOT LIKE '{expression}';
select * or col_name,.. from table_name where col_name LIKE '{expressions}';
select * from table_name where col_name IN (values, values2..,'values',..);select * from table_name wgere col_name IN (select col_name from table_name);
select * from table_name where col_name between value1 and value2;select col_name,. from table_name where col_name between value1 and value2 order by ASC|DESC;select * from table_name where col_name between value1 and value2 and IN (value1,value2..);- NOTE: Can be use NOT BETWEEN and NOT IN.
select col_name as new_col_name from table_name;select col_name as new_col_name,col_name2 as new_col_name2 from table_name;select col_name,concat(col_name,',',col_name...) as new_colname from table_name;-
select class.name,class2.name from class,class2 where {condition}//here class and class2 are different tables and name is their column.
-
(INNER) JOIN: Returns records that have matching values in both tables
-
LEFT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table
-
RIGHT (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left table
-
FULL (OUTER) JOIN: Returns all records when there is a match in either left or right table
-
syntax:
select col_name(s) from table1 {join_type} JOIN table2 ON table1.col_name=table2.col_name ORDER BY col_name ASC|DESC;
select col_name(s) from table1,table2 where {condition} Order By col_name asc|desc;
- union - returns no duplicate / union all - returns also duplicates.
select col_name(s) from table_1 where {condition} union / union all select col_name(s) from table_2 where {condition};
- in group by these functions are often used: COUNT(), MAX(), MIN(), SUM(), AVG().
select col_name(s) from table_name where {condition} GROUP BY col_name ORDER BY col_name ASC|DESC;
- where clause can not be used with aggregate functions. so we use having clause instead of where clause.
SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name WHERE condition GROUP BY column_name(s) HAVING condition ORDER BY column_name(s);
Click below: ⬇️- DDL Commands
- DML Commands
- Click on
Pagesto navigate. - NOTES: SQL PDF NOTE
- NOTES: MYSQL PDF NOTE
-
Contact Me:
+918249587552
Made with Love!